Much has been written about leadership, leadership competencies, and what it takes to be a great leader. Do an internet search for “leadership competencies” and you will find countless lists, such as “The 5 Most Important Competencies” “Top 10 Leadership Competencies”, “How to Develop Google’s Top 7 Leadership Competencies”, etc., etc.
There is no standard, correct list. In each organization, the competencies of effective leaders vary with the industry, business and governmental environment, business strategy and goals, mission and culture. So there is no standard, off-the-shelf competency model for leaders.
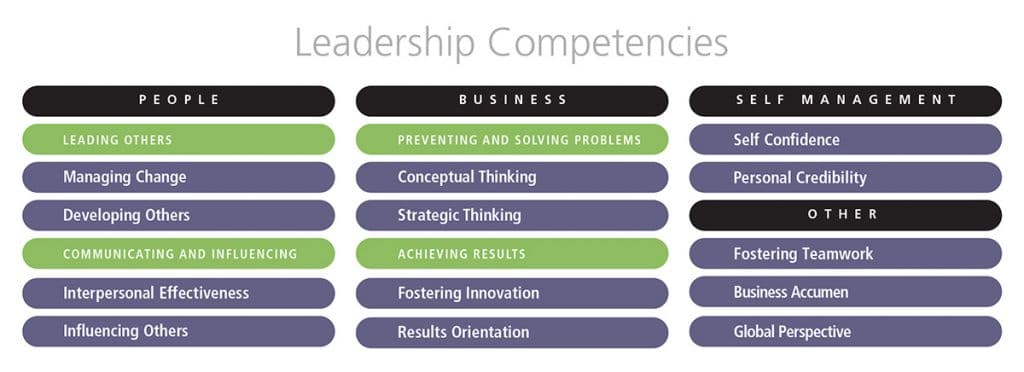
Still, it might be of interest to students of leadership to see one more list of leadership competencies, one based on Workitect’s experience in building models for leaders at all multiple levels in multiple organizations. Our model example includes competencies that have been identified most frequently in models we have built. This is the model, with competencies drawn from the thirty-five competencies in our competency dictionary.
PEOPLE RELATED
Leading Others Cluster
MANAGING CHANGE
Demonstrating support for innovation and for organizational changes needed to improve the organization’s effectiveness; supporting, initiating, sponsoring, and implementing organizational change; helping others to successfully manage organizational change.
DEVELOPING OTHERS
Willingness to delegate responsibility and to work with others and coach them to develop their capabilities.
Communicating and Influencing Cluster
INTERPERSONAL EFFECTIVENESS
The ability to notice, interpret, and anticipate others’ concerns and feelings, and to communicate this awareness empathetically to others.
INFLUENCING OTHERS
The ability to gain others’ support for ideas, proposals, projects, and solutions.
BUSINESS RELATED
Preventing and Solving Problems Cluster
CONCEPTUAL THINKING
Finding effective solutions by taking a holistic, abstract or theoretical perspective.
STRATEGIC THINKING
Analyzing an organization’s competitive position and developing a clear and compelling vision of what the organization needs for success in the future.
Achieving Results Cluster
FOSTERING INNOVATION
Developing, sponsoring or supporting the introduction of new and improved method, products, procedures, or technologies.
RESULTS ORIENTATION
Focusing on the desired end result of one’s own or one’s units work; setting challenging goals, focusing effort on the goals, and meeting or exceeding them.
SELF MANAGEMENT (PERSONAL ATTRIBUTES)
PERSONAL CREDIBILITY
Demonstrated concern that one be perceived as responsible, reliable, and trustworthy.
SELF CONFIDENCE
Faith in one’s own ideas and ability to be successful; willingness to take an independent position in the face of opposition.
OTHERS
FOSTERING TEAMWORK
As a team leader, interest, skill, and success in getting groups to learn to work together cooperatively.
BUSINESS ACUMEN
Ability to perform with insight, acuteness, and intelligence in the areas of commerce and/or industry. Make decisions and act in situations in whicre is not enough information to be certain of outcome or implications of the decision.
GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE
The ability to recognize and address issues that are outside our national perspective.Issues are viewed without any pre-set biases or limitations. Being objective, utilizing a broad framework in making judgments in domestic and international activities. Ability to see the “big picture”.
LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES BY LEVELS
 Many leadership competencies can be observed and developed in lower levels of managers. Having competencies and their behavioral
Many leadership competencies can be observed and developed in lower levels of managers. Having competencies and their behavioral
indicators described by level of job role and level of proficiency can be particularly helpful when the models applied to succession planning. Example: BUILDING COLLABORATIVE RELATIONSHIPS competency.
EXAMPLES OF COMPETENCY MODELS FOR LEADERSHIP POSITIONS
Company Vice Presidents who are presidents of operating divisions of a major manufacturing company.
Project Managers for high-technology company.
DEVELOP A COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK FOR THE ORGANIZATION
A leadership competency model developed for senior management can include the identification of two to six leadership competencies that employees need to demonstrate in order for the organization to achieve its objectives and mission. These “core”competencies help answer the question of “what kind of company do you want our company to be?” Customer Orientation is an example for some organizations. The competencies are then included in the job competency models for all positions in the organization.
TALENT MANAGEMENT APPLICATIONS
Identifying the leadership competencies for an organization serves no purpose unless the competencies are applied to processes for selecting, developing, and retaining talent.
AVAILABLE FROM WORKITECT: AN INTEGRATED SET OF TOOLS FOR SELECTING, DEVELOPING, AND RETAINING LEADERS
 Workitect helps organizations build and implement competency models, frameworks, and applications. Contact me at edward.cripe@workitect.com or 800-870-9490.
Workitect helps organizations build and implement competency models, frameworks, and applications. Contact me at edward.cripe@workitect.com or 800-870-9490.



Hello Ed
This is truly excellent stuff! Thank you. I am building an extremely user-friendly, cost effective (i.e. you don’t need to buy the huge multi-module systems), Excel based integrated talent management toolkit for hi-potential, leadership career pathing, succession planning, etc. – that allows the user-company to input any collection or set of competencies they desire. The tool currently uses a blend of Lominger, Schroeder, and Pink. May I have permission to build the toolkit model using some or all of the competencies you have laid out here? I use some already but I like the mix as you have presented it. I will of course cite you or any other source you require. I hope to hear from you and of course I can send you a working beta version of the existing toolkit (called Career Tracks) if you would like to have a look. I hope to hear from you soon. Thank you and best wishes. Dave
Dave,
Can you send me a regular email about this?
Ed ec@workitect.com